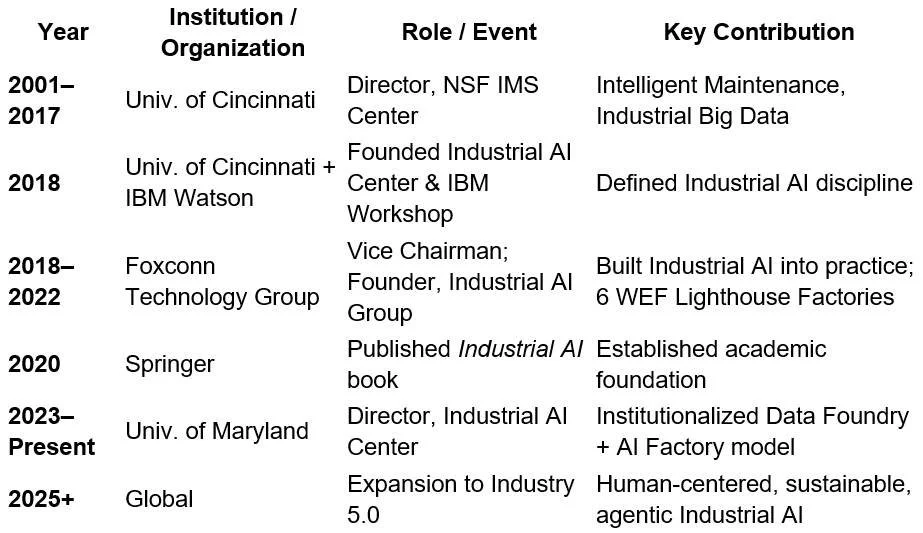
Phase 1 – Foundations of Intelligent Maintenance Systems (2001–2019)
Institution: University of Cincinnati
Center: NSF Industry/University Cooperative Research Center on Intelligent Maintenance Systems (IMS Center)–a multi-campus Industry/University Cooperative Research Center in partnership with University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and University of Texas Austin.
Founder: Prof. Jay Lee
Highlights
Early research in predictive maintenance, prognostics, and machine health management.
Introduced the concept of eMaintenance and Cyber-Physical Systems for Industry.
Pioneered the AI agent Watchdog Agent® architecture for data-driven diagnostics for edge level intelligent maintenance systems in 2001.
Collaborations with over 130 global companies, including Intel, United Technologies, Ford, GM, GE, P&G, Boeing, Caterpillar, and Siemens, Komatsu, Toshiba, Hitachi, Omron, Tokyo, Nissan, Daikin, Mitsubishi Electric, Alstom, Bosch, Samsung, etc.
Conceptual Foundations
“From reliability-centered maintenance to data-driven, self-aware, and predictive industrial systems.”— Jay Lee, Annual Reviews in Control (2013)
Key Achievements
Over 300 industrial case studies and global members.
Over 70+ PhD, 50+ MS, 30+ postdoctoral researchers, and 100+ visiting scholars.
Set the stage for Industrial Big Data and AI-enabled manufacturing research.
Phase 2 – Birth of Industrial AI (2018)
Institution: University of Cincinnati
New Entity: Industrial AI Center (IAI Center)
Milestone Event:
Industrial AI Workshop @ IBM Watson Research Center (2018, New York)
Workshop Objectives
Define “Industrial AI” as a discipline distinct from internet AI.
Discuss AI frameworks for manufacturing, energy, aerospace, and logistics.
Initiate the Industrial AI Framework → a system model bridging data, domain, and decision.
Concept Formalized
“Industrial AI is a systematic discipline that develops AI technologies to perform domain-specific tasks in industrial applications with measurable performance and trustworthiness.” — Jay Lee, Industrial AI: Applications with Sustainable Performance (Springer, 2020)
Core Research Themes
Industrial Big Data management
Edge and Embedded AI
Prognostics and Health Management (PHM)
Human–machine teaming in smart factories
Explainable and safe AI for industry
Key Output
Publication: Industrial AI: Applications with Sustainable Performance (Springer, 2020)
→ Established academic foundations and global adoption of the term Industrial AI.
Phase 3--Industrial AI in Action — The Foxconn Chapter (2018–2022)
Leadership Role
Prof. Jay Lee served as Vice Chairman of Foxconn Technology Group (also known as Hon Hai Precision Industry Co., Ltd.).
Reporting directly to Chairman Terry Gou, he was tasked with leading Foxconn’s Industrial AI and Smart Manufacturing Transformation initiatives.
During this period, he founded and led the Industrial AI Group (IAG) within Foxconn.
Industrial AI Group (IAG) — Core Mission
The IAG was designed as Foxconn’s internal applied AI research and deployment unit, translating the academic Industrial AI framework into real factory systems.
Core objectives:
Build AI-enabled manufacturing platforms (smart scheduling, predictive quality, and real-time optimization).
Deploy Industrial AI technologies across Foxconn’s global network of 1 million+ employees and 30+ manufacturing sites.
Integrate digital twins, IIoT, and data-driven decision-making into Foxconn’s production ecosystem.
Develop new digital manufacturing business models — enabling Foxconn to shift from a “hardware producer” to an “AI-driven solution provider.”
Key Achievements
Development of Six World Economic Forum (WEF) “Lighthouse Factories”
Under Lee’s leadership, Foxconn became one of the world’s top adopters of Industrial AI recognized by the World Economic Forum’s Global Lighthouse Network — factories acknowledged for “digital transformation at scale.”
These “Lighthouse Factories” embodied full Industrial AI integration:
Smart production lines using AI-driven visual inspection and robotics
Edge computing + digital twins for adaptive manufacturing
Data-driven quality prediction systems
Autonomous logistics and AI scheduling systems
Examples include:
Shenzhen Longhua Factory (Smart Manufacturing + Digital Twin)
Zhengzhou Factory (AI-enabled iPhone production lines)
Chengdu and Wuhan sites (industrial data analytics + resilience models)
Mexico and Czech Republic facilities (AI logistics and sustainability integration)
Outcome:
These factories demonstrated measurable improvements — double-digit gains in productivity, yield, and energy efficiency — and became global models for AI-driven industrial operations.
Technology Platforms and Methods Introduced
Industrial AI Framework implemented at scale — integrating Data, Domain, and Deployment.
Data Foundry + AI Factory concepts field-tested for the first time.
AI Twin systems for machine/process simulation and optimization.
Edge AI solutions for inspection, robotics, and equipment diagnostics.
AI + Human collaboration systems for production resilience.
Academic–Industrial Bridge
During his vice chairmanship, Prof. Lee maintained academic collaborations with leading universities and research labs.
Trained a new generation of industrial data scientists and engineers capable of deploying AI in manufacturing contexts.
These efforts helped establish the Industrial AI ecosystem that now extends across academia, industry, and government.
Global Recognition
The World Economic Forum (WEF) and McKinsey highlighted Foxconn’s Industrial AI Group as one of the top global exemplars of Industry 4.0 transformation.
WEF’s 2021–2022 Lighthouse Reports cite Foxconn’s “data-driven continuous learning factories” as a model for Industry 4.0 at scale.
Industrial AI moved from concept to reality, with measurable industrial impact.
Phase 4--Integration into Academic Return (2023–present)
After returning to academia full-time at the University of Maryland, Prof. Lee brought back the:
Industrial AI Group’s methodologies and deployment lessons from Foxconn
WEF Lighthouse factory architectures
Data Foundry + AI Factory model
These are now embedded into UMD’s Industrial AI Center, linking theory, practice, and education.
Transition to University of Maryland (2023–Present)
Institution: University of Maryland, College Park
Center: Industrial AI Center (IAI Center)
Director: Prof. Jay Lee
New Framework: “Data Foundry + AI Factory”
Data Foundry: Converts industrial data into AI-ready representations (data fusion, tokenization, knowledge graphs).
AI Factory: Deploys multi-agent AI systems for process optimization, predictive maintenance, and decision support.
Focuses on the “Four Fs” of industrial AI application:
Factory
Facility
Field
Fleet
Research Areas
Autonomous manufacturing systems
Edge and distributed industrial AI
Resilience and sustainability analytics
Agentic AI for operations and logistics
Partnerships
Continuing collaborations with Komatsu, Foxconn, Mitsubishi Electric, Hitachi Hi-Tech, HIWIN, UMC, ASE, Gestamp, Western Digital, NIST, etc.
Integration with UMD’s Artificial Intelligence Interdisciplinary Institute at Maryland (AIM).
Phase 5--The Present and Future (2025 → )
Goal: Industrial AI as the backbone of Industry 5.0 — human-centered, resilient, and sustainable industrial systems.
Emerging Directions
Agentic Industrial AI – autonomous decision agents for operations.
Cognitive Digital Twins – simulation + reasoning systems using AI.
Trustworthy Industrial AI – safety, verification, and transparency.
Industrial AI Education and Workforce Development – training next-gen industrial data scientists.
Updated Timeline Summary